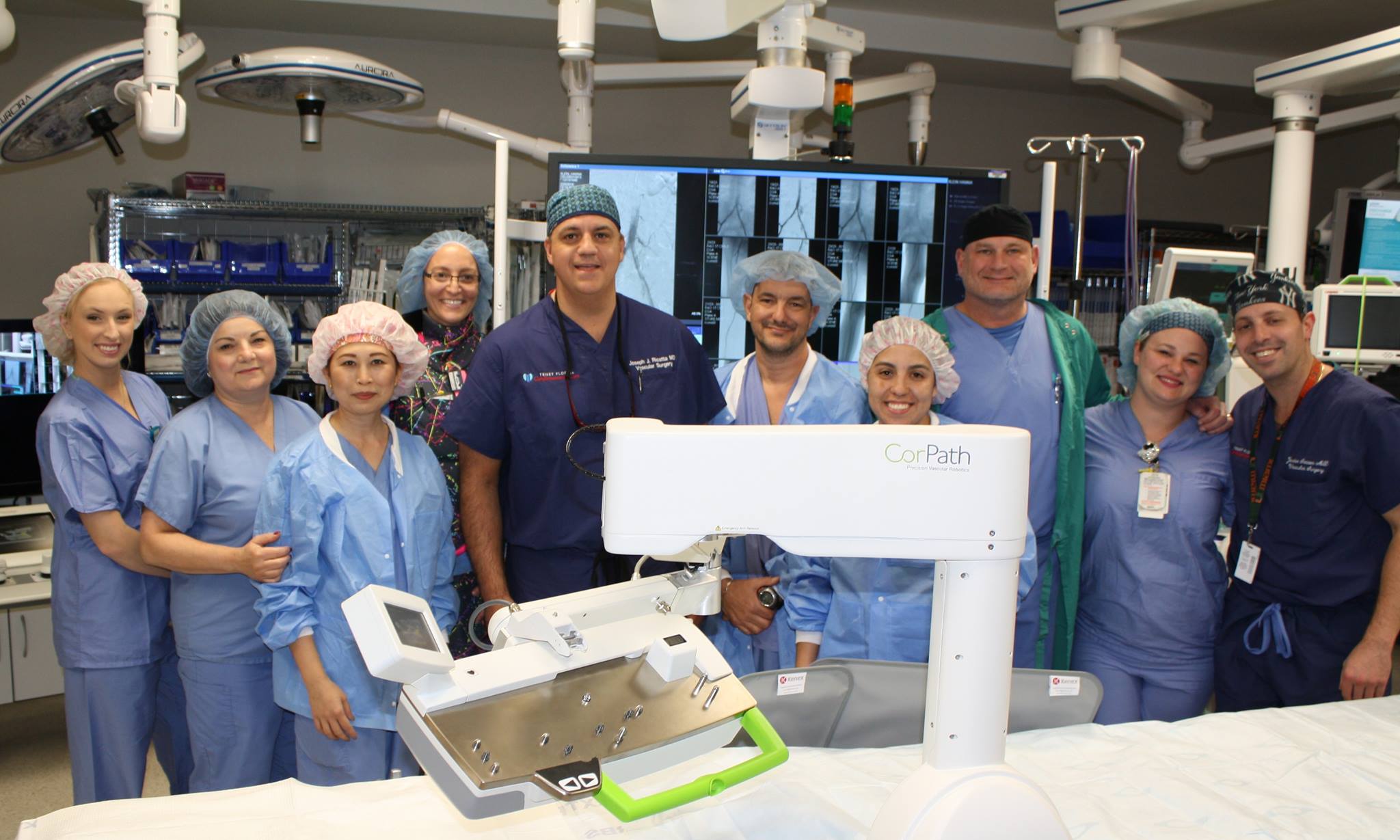
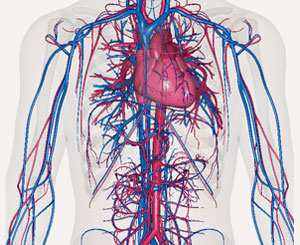
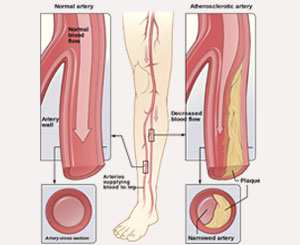
 Stroke is the 3rd leading cause of death in the United States, with greater than 750,000 new cases per year. Eighty percent of strokes are ischemic as a result of lack of blood flow to the brain and the majority of ischemic strokes are due to carotid artery disease, which is also called carotid stenosis.
Stroke is the 3rd leading cause of death in the United States, with greater than 750,000 new cases per year. Eighty percent of strokes are ischemic as a result of lack of blood flow to the brain and the majority of ischemic strokes are due to carotid artery disease, which is also called carotid stenosis.
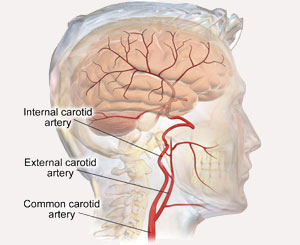
The carotid arteries arise from the aorta just after it leaves the heart and supplies blood to the right and left sides of the brain. Carotid stenosis refers to the narrowing of carotid arteries, usually as a result of fatty, cholesterol deposits called plaque that builds up over time and clogs the carotid arteries. Buildup of plaque in the carotid arteries blocks blood supply to your brain and puts you at an increased risk of stroke.
Risk Factors
The risk factors for developing carotid stenosis are similar to those for developing other forms of vascular disease and include:
-
Age
Smoking
High Blood Pressure
High Cholesterol
Diabetes
Obesity
Sedentary Lifestyle
History of other cardiac or vascular disease
Symptoms
Any adult who has experienced a stroke or transient ischemic attach (TIA)—or “mini-stroke”—should be evaluated for carotid stenosis. However, carotid artery disease develops slowly and most patients with carotid stenosis do not experience symptoms. Sometimes carotid stenosis can be identified when a “swooshing” sound or “bruit” is heard during an examination of the neck with a stethoscope.
Stroke symptoms include:
-
Sudden numbness or weakness in the arms or legs, usually on one side of the body
Numbness, tingling, or weakness of the face, usually around one side of the mouth
Difficulty speaking or understanding speech
Trouble with vision, classically described as “a shade coming down over the eye”
Dizziness or fainting
Sudden onset of a severe headache
Even if symptoms only last for a few seconds, it’s crucial to seek medical attention as soon as possible, as these signs can indicate an increased potential for stroke.
Diagnosis
Since most patients do not have symptoms of carotid disease, it is important to see your doctor for regular physical examinations. If your doctor detects an abnormal sound (“bruit”) in the neck where the carotid arteries are located, this may mean you have carotid artery disease.
Carotid disease is easily checked by a carotid duplex ultrasound, which is non-invasive and painless, and can detect any build-up of plaque or narrowing in the carotid arteries. If carotid stenosis is identified on an ultrasound, then other diagnostic tests—such as a carotid angiogram, CT scan, or MRI—may be required to further delineate the precise location and severity of the narrowing or blockage.
Treatment
Treatment of carotid disease generally comes in three forms: medical management, open surgery, and minimally-invasive carotid stenting. All patients with carotid stenosis—regardless of the severity—should receive “best medical management,” which consists of minimizing risk factors. This is accomplished through medications to control blood pressure and cholesterol (beta-blockers and statins), antiplatelet medications (aspirin, Plavix), smoking cessation, exercise and weight loss, blood sugar control for diabetics, and optimizing any other cardiac or vascular conditions.
The need for further treatment depends upon the severity of the narrowing and whether the patient has symptoms or not. In general, if a patient is ASYMPTOMATIC and has 70% or greater narrowing (stenosis), they will require treatment. If a patient is SYMPTOMATIC and has 50% or greater stenosis, they will require treatment. This treatment is aimed at eliminating the blockage or narrowing within the carotid artery, as well as improving the blood flow to the brain. Both of these treatments can be completed through an open surgery called carotid endarterectomy (CEA) or by utilizing the minimally-invasive endovascular approach of carotid stenting.
Carotid endarterectomy usually requires general anesthesia and involves making an incision along the front of the neck, opening up the carotid artery and removing the plaques. The carotid artery is then sewed closed with the help of a patch. This procedure usually requires a one-night stay in the hospital and patients can expect to return to normal activity within four weeks.
Carotid stenting is performed under local anesthesia through a small needle puncture in the groin artery. A catheter is then advanced into the carotid artery and a small balloon is inserted at the location of the plaque and inflated to widen the artery. A stent is then placed across the plaque to keep the artery open and prevent it from narrowing. This procedure also requires a one-night stay in the hospital; however, patients can expect to a recovery time of only one or two days.
Both treatment options are extremely effective when completed by an experienced surgeon, but it’s important to remember that treatment for carotid disease must be individualized for each patient. Some patients benefit more from surgery, while others fare better with stenting. In short, it is vital for patients to seek the consultation of a vascular surgeon who is practiced and knowledgeable in both areas.